
In today’s digital-first society, cybersecurity has emerged as one of the most important business issues. Organizations deal with sophisticated cyberattacks on a daily basis, ranging from insider threats to AI-generated deepfakes to ransomware and phishing. The worrying truth is that attackers are employing AI to carry out increasingly accurate and scalable attacks. Businesses need to come up with an equally clever defense to combat this.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity fills this gap, serving as the foundation of next-generation defense rather than a supplementary technology. AI learns, anticipates, and adjusts to new dangers at machine speed in addition to detecting known ones. AI-driven cybersecurity is now necessary—not optional—for businesses hoping to prosper in a more hostile digital landscape.
Essential Elements of Cybersecurity Driven by AI
Cybersecurity is becoming more proactive, flexible, and effective thanks to artificial intelligence. The following are the key characteristics propelling the next security generation:
-
Real-Time Threat Detection: AI keeps an eye on endpoints, networks, and cloud services all the time, quickly spotting irregularities and zero-day threats.
-
Predictive Intelligence: Machine learning algorithms predict possible intrusions, foresee the actions of hackers, and stop breaches before they happen.
-
Real-Time Threat Detection: AI keeps an eye on endpoints, networks, and cloud services all the time, quickly spotting irregularities and zero-day threats.
- Behavioral analytics: AI can identify insider threats, credential abuse, and questionable patterns that traditional technologies frequently overlook by examining user and device activity.
- ByteCipher’s invention: Multi-AI Agent Collaboration For a single defense grid, several specialized AI agents collaborate to safeguard each tier, including endpoint, identity, fraud, and data.
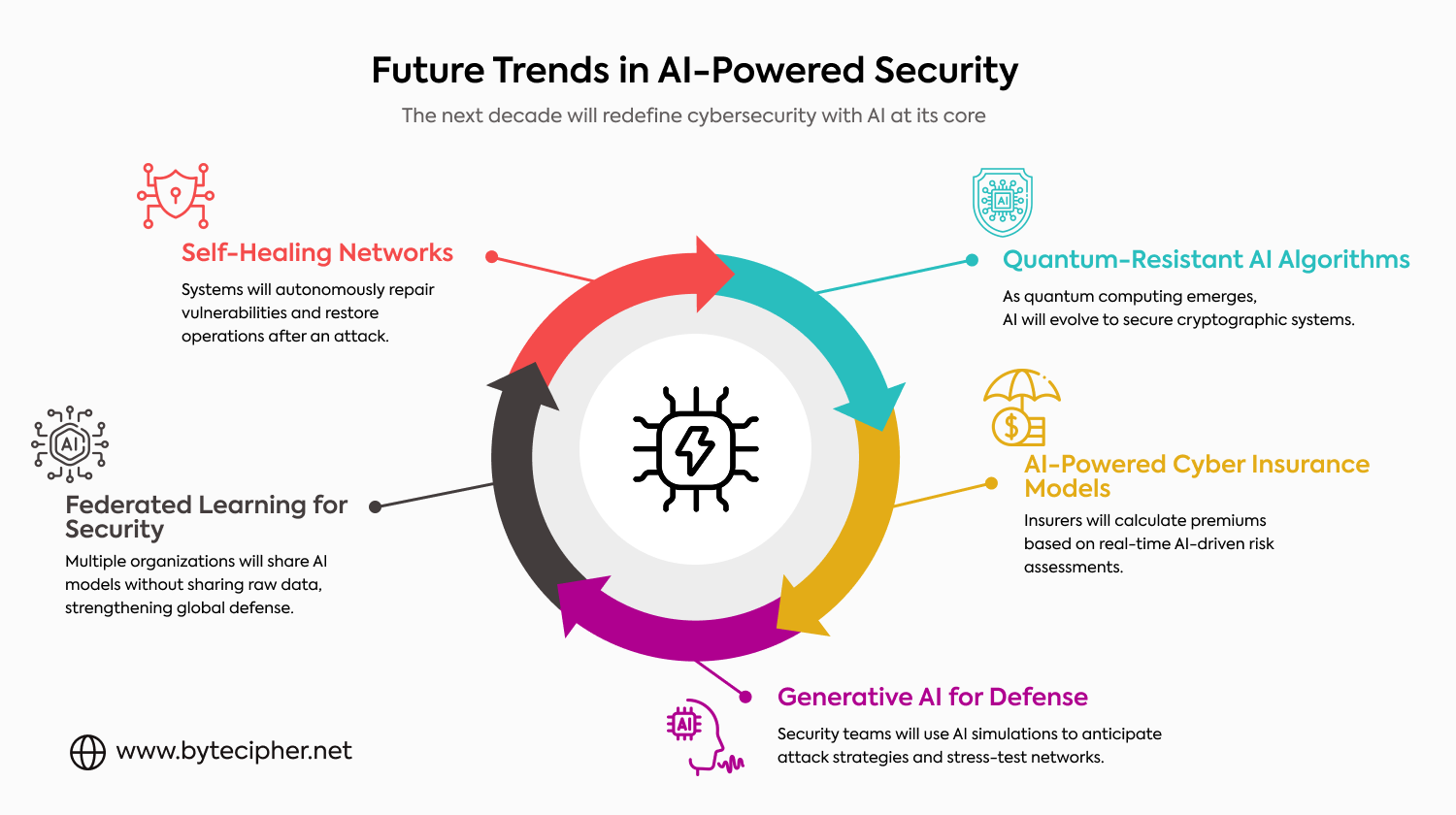
- Generative AI for Security Simulation: AI helps businesses proactively address vulnerabilities, stress-test networks, and model possible attack scenarios.
- Adaptive Learning: AI changes to match the strategies of attackers, guaranteeing that defenses against novel and sophisticated attacks stay effective.
- Cloud & IoT Security Integration: AI protects billions of IoT devices and cloud-native apps, extending security to hybrid settings.
- Data Privacy & Compliance Support: This service protects sensitive data while guaranteeing compliance with international laws such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS.
-
Intelligence-Led Cyber Defense (ByteCipher focus): a combination of skilled human analysts with AI automation for ongoing threat hunting, monitoring, and quicker recovery.
The Changing Environment for Threats
The cyber battlefield has changed significantly:
- AI-Powered Attacks: Hackers are using machine learning to create deepfake movies for fraud, create highly targeted phishing emails, and even use adaptive malware to get past conventional protections.
- Runsomware as a Service (RaaS): Ransomware kits are now available from cybercrime organizations, allowing even inexperienced attackers to carry out destructive attacks.
- Supply Chain Breach: Attackers enter through software upgrades and outside vendors rather than going straight after businesses.
- Data Explosion: Security teams deal with massive amounts of data due to the billions of linked devices, which makes manual threat detection unfeasible.
While AI offers proactive intelligence—identifying irregularities, anticipating threats, and thwarting assaults before harm is done—traditional rule-based defense is reactive and slow.
The Impact of AI on Cybersecurity
A paradigm shift in how businesses protect their systems is brought about by AI.
1. Scalable Threat Detection
Across networks, cloud platforms, and endpoints, AI can handle millions of events each second. Anomaly detection can be used to identify anomalous activity, such as a device interacting with dubious services or a user accessing files at strange times.
2. Anticipatory Intelligence
Machine learning algorithms use global threat intelligence feeds, hacker activity patterns, and historical data to predict possible attacks.
3. Response by Automated
Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered security solutions can instantly block dangerous IP addresses, isolate hacked devices, and terminate questionable accounts without awaiting human permission.
4. Analytical Behavior
In contrast to antiviral software that relies on signatures, AI analyzes system and user activity. AI can identify, for instance, when an employee’s account unexpectedly tries to move huge amounts of money, even if the attacker has legitimate credentials.
5. Supplementing Human Analysts
AI empowers cybersecurity professionals rather than replaces them. AI helps analysts focus on real risks by removing false positives and noise.
AI Security’s Business Case
In addition to safety, businesses that use AI in cybersecurity also gain competitive advantage and business resiliency.
- Lower Breach Costs: Financial and reputational harm are reduced through quicker identification.
- Improved Compliance: GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS compliance is facilitated by automated monitoring.
- Customer Trust: Users are more confident and loyal in a secure online environment.
- Efficiency in Operations: AI reduces the workload of IT workers by automating repetitive security operations.
Artificial intelligence security is a boardroom concern for digital-first businesses, not just an IT expenditure.
The Difficulties of AI in Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence improves cyber security, but it also has drawbacks and hazards of its own. Adversarial AI, in which hackers utilize AI to create complex attacks that can get past automated defenses, is a significant problem. This effectively creates a battlefield between AI and AI. Another issue is false positives, which can slow down real responses if AI models are not trained properly.
AI also suffers from data reliance in order to function well, it needs vast amounts of varied, high-quality data. Concerns about security, privacy, and the moral use of private data are raised by this. Furthermore, it might be challenging for enterprises to audit or explain the reasoning behind specific security decisions because many AI models function as “black boxes.”
A balanced strategy that combines AI-driven security with human expertise, ensures transparency, and enforces ethical governance is necessary for firms to overcome these obstacles. The development of long-term confidence in cybersecurity solutions will depend on this human-AI collaboration.
Cybersecurity Solutions Powered by AI from ByteCipher
We at ByteCipher Pvt. Ltd. provide cutting-edge, AI-powered cybersecurity frameworks that instantly safeguard businesses.
Multiple AI Agent Protection
In place of a single AI, we use cooperative multi-agent AI systems, each with a distinct area of expertise, such as access control, fraud detection, or endpoint security. When combined, they form an intelligent defense grid.
Enhancement of Security through Generative AI
By simulating future cyberattack patterns using generative AI, we enable organizations to get ready before actual threats materialize.
Artificial Intelligence-Powered Data Security
Large datasets from cloud, IoT, and on-premises systems are analyzed by our AI engines, which find anomalies that are unseen to humans.
Services for Security Led by Intelligence
Our cybersecurity services offer incident response customized to customer needs, predictive threat hunting, and round-the-clock monitoring by fusing AI techniques with human knowledge.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity has evolved into a dynamic conflict between intelligent systems rather than a static defense. Businesses can no longer rely only on human surveillance or outdated tools against increasingly sophisticated attackers. The agility, intelligence, and automation that AI offers are essential for fending against changing threats.
We at ByteCipher are at the forefront of developing multi-agent, intelligence-led, AI-powered cybersecurity solutions to keep businesses resilient, compliant, and prepared for the future. AI is not merely a component of protection in the age of next-generation cybersecurity; it is the defense itself. This is the plain message.


